The structure activity relationship of adrenergic drugs is as follows. Indirect acting drugs act by releasing norepinephrine from adrenergic nerve endings.
Adrenergic Drugs Basicmedical Key
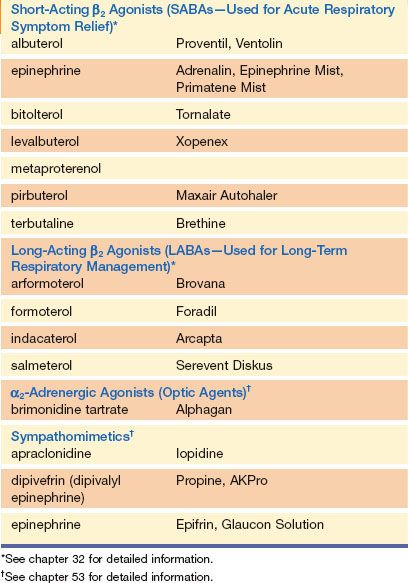
Adrenergic drugs such as metaraminol Aramine isoproterenol Isuprel and ephedrine are synthetic adrenergic drugs.
. The nurse would anticipate administering drugs that generally block all adrenergic receptor sites to treat a. It is usually defined as the plasma drug concentration necessary to produce 50 of that drugs maximal effect called the EC50. Relaxation of smooth muscles of the bronchi e.
It equally blocks alpha 1 and alpha 2 adrenoceptors. In comparing two drugs the drug with the lower EC50 is said to be more potent or to have a higher potency. Low doses have dopaminergic effects resulting in dilation of blood vessels in the brain heart kidneys and mesentery increasing blood flow to these areas.
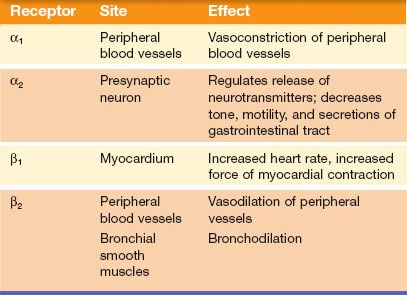
Alpha -adrenergic receptor activation relaxes gastrointestinal smooth muscle beta-adrenergic receptor activation relaxes gastrointestinal smooth muscle alpha-2 agonists act indirectly by reducing acetylcholine release presynaptic effect. These drugs bind to more of the adrenergic receptors when administered at higher doses ie can lose selectivity. It produces rapid and short lasting alpha adrenergic blockade.
Adrenergic receptor activity is stimulated causing improved cardiac contractility which is desirable in HF. Can dilate blood vessels in the brain heart kidneys and mesentery which increases blood flow to these areas dopaminergic receptor activity. Improve cardiac contractility and output beta1-adrenergic receptor activity.
It is the most potent alpha blocker. This adrenergic receptor subtype is expressed on vascular smooth muscle at sites some distance away from sympathetic nerve terminals and produces vasoconstrictor responses when stimulated by circulating catecholamines such as epinephrine. The primary reason for preferring phentolamine as the alpha adrenergic blocker for performing diagnostic test for pheochromocytoma is.
In contrast β-ARs respond potently to isoproterenol and are less sensitive to epinephrine and norepinephrine. These hormones which are also known as noradrenaline and adrenaline are secreted by the adrenal gland hence their association with the term adrenergic. Increased heart rate is one of the effects of adrenergic drugs.
ACTIONS Generally adrenergic drugs produce one or more of the following responses in varying degrees. Many of the beta-adrenergic blockers are nonselective blocking both beta1 and beta2 receptors. Adrenergic receptors were originally divided into two major groups.
Which response by the nurse is appropriate. Increased heart rate b. Drug potency is also commonly used to compare two drugs.
Adrenergic drug any of various drugs that mimic or interfere with the functioning of the sympathetic nervous system by affecting the release or action of norepinephrine and epinephrine. Adrenergic blocking drugs because of their clinical effects are also known as a. α- and β-adrenoceptors ARs.
Adrenergic agonists are autonomic nervous system drugs that stimulate the adrenergic receptors of the sympathetic nervous system SNS either directly by reacting with receptor sites or indirectly by increasing norepinephrine levels. Baroreceptorvagal response and increased release of acetylcholine onto the heart in response to the vasopressor effect of NE. Epinephrine binds to all of the adrenergic receptors.
An adrenergic agonist is also called a sympathomimetic because it stimulates the effects of SNS. Increased use of glucose c. α-ARs demonstrate weak responses to the synthetic agonist isoproterenol but are very responsive to epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Potent dopaminergic as well as beta1- and alpha1-adrenergic receptor activity Low dosages. The nurse is aware that adrenergic drugs produce effects similar to which of these nervous systems. The following are key clinical indications of various adrenergic drugs.
Two of the proteins that are phosphorylated in this process breakdown glycogen and stop. Sympathetic nervous system 2 When an adrenergic drug stimulates beta1-adrenergic receptors the result is an increased force of contraction which is known as what type of effect. Adrenergic compounds are synthesized within the adrenal medulla and neuronal endings commencing with tyrosine which is sequentially converted to dopamine norepinephrine or epinephrine depending on the presence or absence of specific converting enzymes.
Modification takes place at amino C α C β C 3 and C 4 atoms to produce newer drugs. The response would be. The maximum level of receptor binding for a.
Decreased pulse rate and bronchoconstriction. It has no additional Beta adrenergic blocking property. One of the first beta-adrenergic blockers beta blocker was propranolol Inderal.
Direct acting drugs act directly on adrenergic receptors to elicit responses. Thebinding of the adrenergic receptor causes a series of reactions that eventually results in a characteristic response. Dopamine binds to the alpha-1 alpha 2 beta-1 receptors and also dopamine receptors.
Beta-adrenergic agonist responses -cardiac stimulation heart rate -bronchial GI and uterine smooth muscle relaxation -glycogenolysis blood sugar Dopaminergic receptors -an additional adrenergic receptor -stimulated by dopamine -causes dilation of the following blood vessels resulting in blood flow. Adrenergic drugs generally produce which of the following responses. A nurse administers propranolol hydrochloride Inderal.
Sympathetic nervous system stimulation also results in bronchodilation dilated pupils and decreased gastrointestinal mobility depending upon which receptors are stimulated. The most common adverse effects of alpha-2 receptor agonists are sedation and fatigue22 The adverse effects of alpha-1 agonists include hypertension tachycardia or other dysrhythmias increased cardiac demand and subcutaneous ischemia at the site of injection.

Adrenergic Drugs Basicmedical Key

Adrenergic Agonists And Antagonists Neuropharmacology Goodman And Gilman Manual Of Pharmacology And Therapeutics

Adrenergic Drugs Adrenergic Receptors Are Divided Into Two Major Types According To Drug Potency On The Receptors Alpha A Adrenergic Receptors Ppt Download

0 Comments